Using Eloquent models with the Firebase Realtime Database
When working with Laravel, we have multiple ways of implementing real time messages / event broadcasting to our application, thanks to the Redis or Pusher integration in the framework.
But what if we want to persist the realtime data in some kind of database?
If you, for example, want to build a chat with pusher, you will notice that the messages don't get stored and will be gone after reloading your chat system. That's where Firebase comes into play by offering a "Realtime Database" (alongside many other great solutions).
Let's build a simple Todo app that will synchronize the Laravel models with the Firebase Realtime Database.
The free plan (called "Spark") comes with very generous limitations to get you started:
| Feature | Limitation |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous connections | 100 |
| GB stored | 1 GB |
| GB transferred | 10 GB |
Getting started #
To begin experimenting with Firebase, start by creating a project over at the Firebase Console.
After you logged in with your Google account, create a new project.
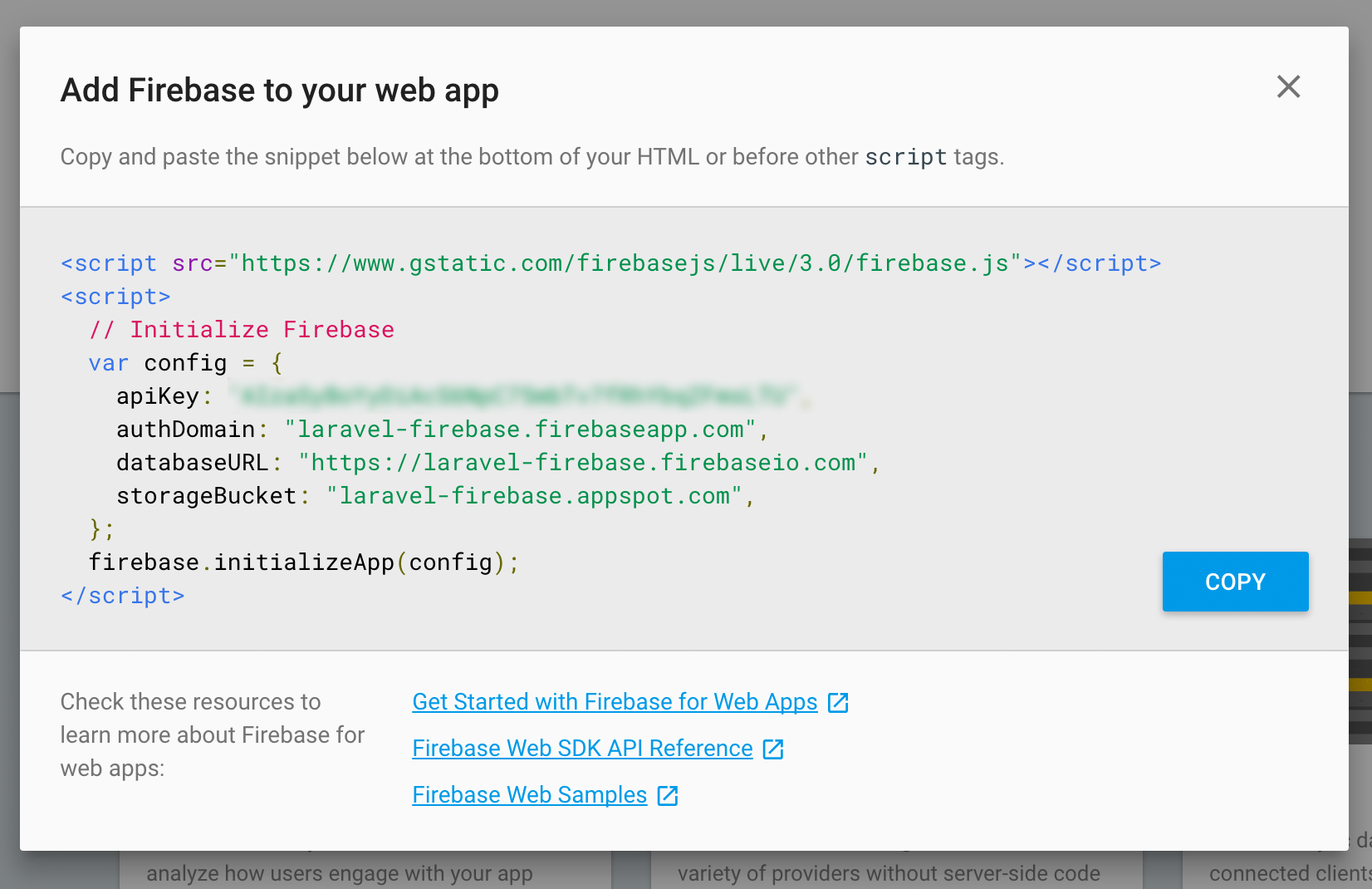
When the project was created successfully, press "Add Firebase to your web app" and a popup will come up, showing you the API credentials you will use to access Firebase.
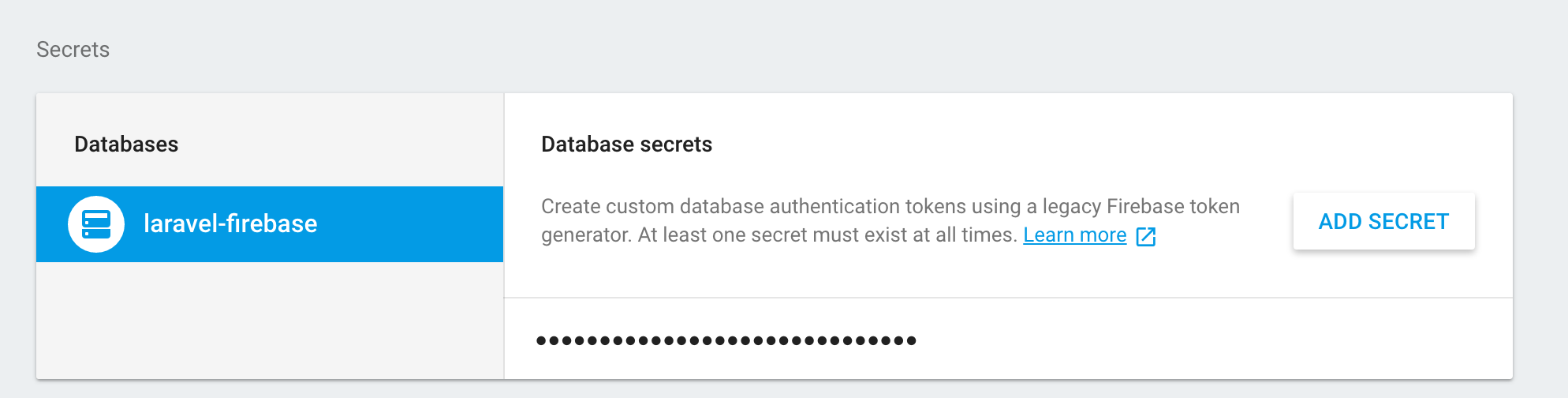
Because your Laravel app will need to be authenticated with Firebase in order to write data into it, you also want to copy the database secret you can obtain from select "Project settings / database":
Now that you have gathered all relevant information from Firebase, lets move on with the Laravel integration.
Laravel preparation #
Since we want to build a Todo app I created a simple table schema for it, to use for this example:
Schema::create('todos', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('task');
$table->boolean('is_done')->default(false);
$table->timestamps();
});
Laravel integration #
Install the Firebase Sync trait with this command:
composer require mpociot/laravel-firebase-sync
Next, create a new section in your config/services.php file, that will look like this:
'firebase' => [
'api_key' => 'api key taken from firebase',
'auth_domain' => 'auth domain taken from firebase',
'database_url' => 'database uri taken from firebase',
'secret' => 'db secret taken from firebase',
'storage_bucket' => 'storage bucket taken from firebase',
]
Create a new Todo model, which will make use of the Firebase synchronization:
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Mpociot\Firebase\SyncsWithFirebase;
class Todo extends Model
{
/**
* Automatically persist the model in the Firebase realtime
* database, whenever it gets created/updated/deleted
*/
use SyncsWithFirebase;
protected $fillable = ['task', 'is_done'];
protected $visible = ['id', 'task', 'is_done'];
}
By adding the SyncsWithFirebase trait to your model, the model creation, updates and deletes will be reflected in the Firebase Realtime Database automatically.
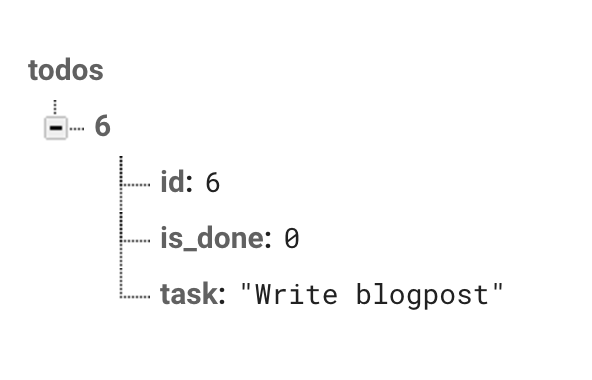
You can already see it in action by using php artisan tinker and creating a Todo manually:
\App\Todo::create([
'task' => 'Write blog post',
'is_done' => false
]);
When looking at the Firebase database console, you will see that the JSON representation of the model is already stored in Firebase:
Adding the Firebase JS API #
To make use of the Firebase Realtime features, we will make use of VueJS and the Firebase JS SDK.
Create a view for your todo list containing a simple form to create new todos, and a table to list all existing todos:
<h1>Create task</h1>
<input type="text" v-model="task" placeholder="Task" />
<a @click="createTodo()">Save</a>
<table class="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Task</th>
<th>Done</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<template v-for="todo in todos">
<tr>
<td>
@{{todo.task}}
</td>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="todo.is_done" />
</td>
</tr>
</template>
</tbody>
</table>
Now hook it up with a little VueJS app:
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.0.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/1.0.25/vue.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/live/3.0/firebase.js"></script>
<script>
// Initialize Firebase
var config = {
apiKey: "{{ config('services.firebase.api_key') }}",
authDomain: "{{ config('services.firebase.auth_domain') }}",
databaseURL: "{{ config('services.firebase.database_url') }}",
storageBucket: "{{ config('services.firebase.storage_bucket') }}",
};
firebase.initializeApp(config);
new Vue({
el: 'body',
data: {
task: '',
todos: []
},
ready: function() {
var self = this;
// Initialize firebase realtime database.
firebase.database().ref('todos/').on('value', function(snapshot) {
// Everytime the Firebase data changes, update the todos array.
self.$set('todos', snapshot.val());
});
},
methods: {
/**
* Create a new todo and synchronize it with Firebase
*/
createTodo: function() {
var self = this;
// For the sake of simplicity, I'm using jQuery here
$.post('/todo', {
_token: '{!! csrf_token() !!}',
task: self.task,
is_done: false
});
this.task = '';
}
}
});
</script>
And last but not least, create the POST /todo route and controller, which will look like this:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Todo;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Http\Requests;
class TodoController extends Controller
{
/**
* @param Request $request
* @return \Illuminate\Http\RedirectResponse|\Illuminate\Routing\Redirector
*/
public function store(Request $request)
{
Todo::create($request->all());
return redirect('/');
}
}
Simple enough!
And that's it - now when you open up the Todo list in two different browser tabs, creating a Todo entry in one tab should automatically synchronize with Firebase and reload the table in your second browser tab.
With this setup you will have the best of both worlds - a realtime database through Firebase and also all data inside your mySQL database to use with Laravels Eloquent ORM.
Please note, that this is not a real "synchronization", as the data manipulated in Firebase will not get synchronized back to your Laravel app.
You can take a look at the full code of the example application at the Github repository.